What Is The Template Of The Pcr
What Is The Template Of The Pcr - (2) annealing, in which short dna. Pcr is a technique that allows researchers to quickly create many copies of a specific region of dna in vitro. What is the polymerase chain reaction (pcr)? Polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is a technique used in medicine and molecular biology research to make many thousands or even millions of copies of a section of dna, such as a specific. The essential components of a pcr reaction include a dna template containing the target sequence, dna primers that flank the target sequence, dna polymerase (such as. The source of dna can include genomic dna (gdna), complementary dna (cdna) or plasmids. One unit incorporates 10 nmol of total deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates into acid precipitable dna in 30 minutes at 74 °c. Pcr (polymerase chain reaction) is a method used in molecular biology to make millions of physical copies of a specific dna sequence, for example, a gene. Each pcr assay requires the presence of template dna, primers, nucleotides, and dna polymerase. Amplification is achieved by a series of three steps: A standard polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is an in vitro method that allows a single, short region of a dna molecule (single gene perhaps) to be copied multiple times by taq. The dna polymerase is the key enzyme that links individual nucleotides together. The source of dna can include genomic dna (gdna), complementary dna (cdna) or plasmids. Polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is a technique used in medicine and molecular biology research to make many thousands or even millions of copies of a section of dna, such as a specific. Pcr is efficient, rapid and. [1] [4] thermostability can resist irreversible alterations in chemical and physical. The essential components of a pcr reaction include a dna template containing the target sequence, dna primers that flank the target sequence, dna polymerase (such as. One unit incorporates 10 nmol of total deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates into acid precipitable dna in 30 minutes at 74 °c. Amplification is achieved by a series of three steps: Polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is a reaction in which specific regions of dna are amplified in vitro. A standard polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is an in vitro method that allows a single, short region of a dna molecule (single gene perhaps) to be copied multiple times by taq. Pcr is efficient, rapid and. The dna polymerase is the key enzyme that links individual nucleotides together. Pcr is a procedure that selectively focuses on a minuscule segment of. Pcr is efficient, rapid and. Pcr primers are designed to bind (via sequence complementarity) to sequences that flank the region of interest. Polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is a technique used in medicine and molecular biology research to make many thousands or even millions of copies of a section of dna, such as a specific. The essential components of a pcr. (2) annealing, in which short dna. Amplification is achieved by a series of three steps: Each pcr assay requires the presence of template dna, primers, nucleotides, and dna polymerase. One unit incorporates 10 nmol of total deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates into acid precipitable dna in 30 minutes at 74 °c. It is one of the most widely utilized techniques in the. Pcr is efficient, rapid and. The essential components of a pcr reaction include a dna template containing the target sequence, dna primers that flank the target sequence, dna polymerase (such as. One unit incorporates 10 nmol of total deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates into acid precipitable dna in 30 minutes at 74 °c. Polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is a reaction in which specific. It is one of the most widely utilized techniques in the. Pcr (polymerase chain reaction) is a method used in molecular biology to make millions of physical copies of a specific dna sequence, for example, a gene. Polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is a reaction in which specific regions of dna are amplified in vitro. (2) annealing, in which short dna.. The source of dna can include genomic dna (gdna), complementary dna (cdna) or plasmids. One unit incorporates 10 nmol of total deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates into acid precipitable dna in 30 minutes at 74 °c. Each pcr assay requires the presence of template dna, primers, nucleotides, and dna polymerase. A standard polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is an in vitro method that allows. Pcr is efficient, rapid and. (2) annealing, in which short dna. Pcr is a procedure that selectively focuses on a minuscule segment of dna in a test tube. Amplification is achieved by a series of three steps: Polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is a common molecular biology technique that enables researchers to make multiple copies of a specific region of dna. Amplification is achieved by a series of three steps: [1] [4] thermostability can resist irreversible alterations in chemical and physical. Pcr is a technique that allows researchers to quickly create many copies of a specific region of dna in vitro. (2) annealing, in which short dna. A standard polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is an in vitro method that allows a. The dna polymerase is the key enzyme that links individual nucleotides together. Amplification is achieved by a series of three steps: A standard polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is an in vitro method that allows a single, short region of a dna molecule (single gene perhaps) to be copied multiple times by taq. Pcr is a procedure that selectively focuses on. The source of dna can include genomic dna (gdna), complementary dna (cdna) or plasmids. Pcr is efficient, rapid and. Polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is a reaction in which specific regions of dna are amplified in vitro. Pcr primers are designed to bind (via sequence complementarity) to sequences that flank the region of interest. Pcr (polymerase chain reaction) is a method. Polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is a reaction in which specific regions of dna are amplified in vitro. Pcr is a procedure that selectively focuses on a minuscule segment of dna in a test tube. The dna polymerase is the key enzyme that links individual nucleotides together. It is one of the most widely utilized techniques in the. What do i need to perform. Polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is a technique used in medicine and molecular biology research to make many thousands or even millions of copies of a section of dna, such as a specific. A standard polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is an in vitro method that allows a single, short region of a dna molecule (single gene perhaps) to be copied multiple times by taq. Each pcr assay requires the presence of template dna, primers, nucleotides, and dna polymerase. The essential components of a pcr reaction include a dna template containing the target sequence, dna primers that flank the target sequence, dna polymerase (such as. Pcr is efficient, rapid and. Polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is a common molecular biology technique that enables researchers to make multiple copies of a specific region of dna. Pcr (polymerase chain reaction) is a method used in molecular biology to make millions of physical copies of a specific dna sequence, for example, a gene. The source of dna can include genomic dna (gdna), complementary dna (cdna) or plasmids. (2) annealing, in which short dna. Amplification is achieved by a series of three steps: One unit incorporates 10 nmol of total deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates into acid precipitable dna in 30 minutes at 74 °c.What are the properties of PCR (template) DNA?
PCR Template PDF
What Is The Template Of The Pcr
Pcr Template Concentration
What Is The Template Of The Pcr
Pcr Template Amount Addgene What is Polymerase Chain Reaction Pcr
What Is The Template Of The Pcr
Setting up for Success How Do I Ensure I Have the Right Template for
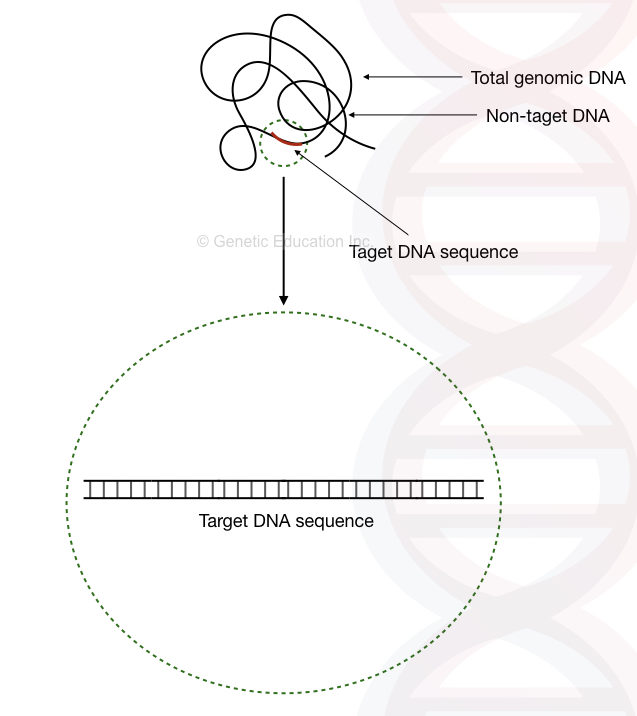
What are the properties of PCR (template) DNA? Education
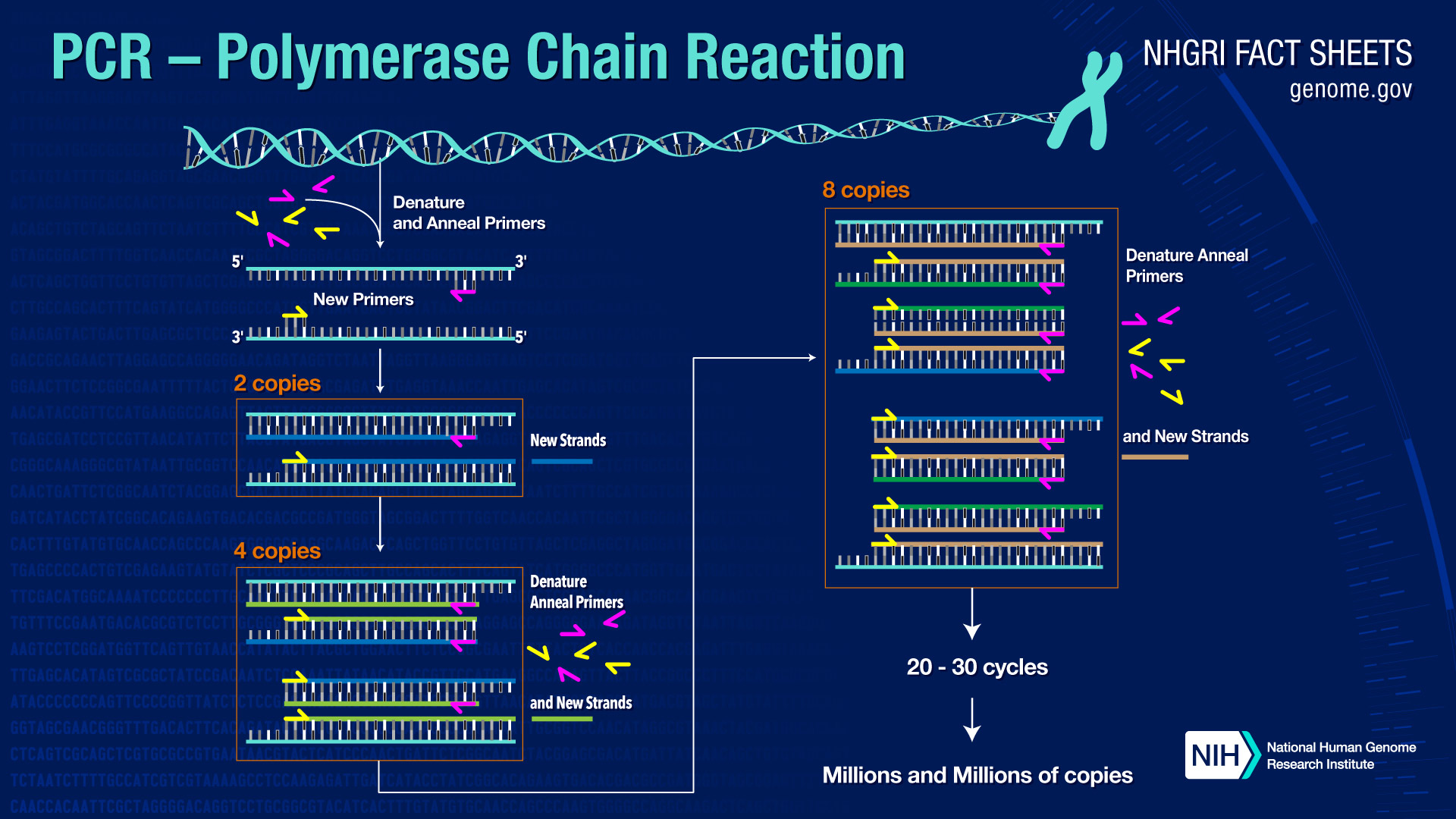
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Fact Sheet
[1] [4] Thermostability Can Resist Irreversible Alterations In Chemical And Physical.
What Is The Polymerase Chain Reaction (Pcr)?
Pcr Primers Are Designed To Bind (Via Sequence Complementarity) To Sequences That Flank The Region Of Interest.
Pcr Is A Technique That Allows Researchers To Quickly Create Many Copies Of A Specific Region Of Dna In Vitro.
Related Post: