Template Matching Theory
Template Matching Theory - There are six main theories of pattern recognition: The hypothesis that pattern recognition proceeds by comparing an incoming sensory stimulation pattern to mental images or representations of patterns (templates) until a match is found. Template matching is the process by which the mind identifies objects by comparison to [a particular kind of] stored mental representation. The page discusses different theories of object recognition: According to the theory, the mind carries around a vast storehouse of. This mechanism plays a crucial role in how we identify objects, faces, and other stimuli, enabling quick recognition by matching incoming information to existing knowledge. Template matching, prototype matching, and feature analysis. Template matching involves comparing objects to stored templates, but it. The hypothesis postulating that pattern recognition progresses by comparing an input sensory arousal pattern to cognitive pictures or symbolizations of patterns until a match is located. This theory is largely considered too simplistic, because the same stimulus can be viewed from multiple perspectives, thereby altering the input pattern, and. The hypothesis that pattern recognition proceeds by comparing an incoming sensory stimulation pattern to mental images or representations of patterns (templates) until a match is found. This mechanism plays a crucial role in how we identify objects, faces, and other stimuli, enabling quick recognition by matching incoming information to existing knowledge. For example, the classic template matching theory assumes that an incoming visual image is compared with a library of prestored dimensionally isomorphic images, each of which has a name already associated with it. Template matching involves comparing objects to stored templates, but it. Template matching is a cognitive process where an individual recognizes patterns by comparing sensory input against stored mental templates or prototypes. Template matching, prototype matching, and feature analysis. The hypothesis postulating that pattern recognition progresses by comparing an input sensory arousal pattern to cognitive pictures or symbolizations of patterns until a match is located. Template matching is the process by which the mind identifies objects by comparison to [a particular kind of] stored mental representation. The page discusses different theories of object recognition: There are six main theories of pattern recognition: Template matching is the process by which the mind identifies objects by comparison to [a particular kind of] stored mental representation. According to the theory, the mind carries around a vast storehouse of. Template matching involves comparing objects to stored templates, but it. The page discusses different theories of object recognition: There are six main theories of pattern recognition: According to the theory, the mind carries around a vast storehouse of. Template matching, prototype matching, and feature analysis. The application of these theories in everyday life is not mutually exclusive. For example, the classic template matching theory assumes that an incoming visual image is compared with a library of prestored dimensionally isomorphic images, each of which has a name. The best match of the incoming image with one of the stored library of templates determines which. According to the theory, the mind carries around a vast storehouse of. There are six main theories of pattern recognition: Feature matching theory posits that objects are recognized by comparing their features to stored representations in memory, while template theory suggests that objects. The page discusses different theories of object recognition: The best match of the incoming image with one of the stored library of templates determines which. Feature matching theory posits that objects are recognized by comparing their features to stored representations in memory, while template theory suggests that objects are recognized by matching incoming stimuli to specific templates or prototypes stored. The page discusses different theories of object recognition: Template matching is a cognitive process where an individual recognizes patterns by comparing sensory input against stored mental templates or prototypes. For example, the classic template matching theory assumes that an incoming visual image is compared with a library of prestored dimensionally isomorphic images, each of which has a name already associated. Template matching, prototype matching, and feature analysis. Template matching is the process by which the mind identifies objects by comparison to [a particular kind of] stored mental representation. For example, the classic template matching theory assumes that an incoming visual image is compared with a library of prestored dimensionally isomorphic images, each of which has a name already associated with. This theory is largely considered too simplistic, because the same stimulus can be viewed from multiple perspectives, thereby altering the input pattern, and. This mechanism plays a crucial role in how we identify objects, faces, and other stimuli, enabling quick recognition by matching incoming information to existing knowledge. The hypothesis that pattern recognition proceeds by comparing an incoming sensory stimulation. Feature matching theory posits that objects are recognized by comparing their features to stored representations in memory, while template theory suggests that objects are recognized by matching incoming stimuli to specific templates or prototypes stored in memory. This mechanism plays a crucial role in how we identify objects, faces, and other stimuli, enabling quick recognition by matching incoming information to. There are six main theories of pattern recognition: The hypothesis that pattern recognition proceeds by comparing an incoming sensory stimulation pattern to mental images or representations of patterns (templates) until a match is found. This theory is largely considered too simplistic, because the same stimulus can be viewed from multiple perspectives, thereby altering the input pattern, and. The page discusses. Template matching involves comparing objects to stored templates, but it. Template matching, prototype matching, and feature analysis. This mechanism plays a crucial role in how we identify objects, faces, and other stimuli, enabling quick recognition by matching incoming information to existing knowledge. The hypothesis postulating that pattern recognition progresses by comparing an input sensory arousal pattern to cognitive pictures or. According to the theory, the mind carries around a vast storehouse of. The best match of the incoming image with one of the stored library of templates determines which. Template matching is a cognitive process where an individual recognizes patterns by comparing sensory input against stored mental templates or prototypes. The page discusses different theories of object recognition: For example, the classic template matching theory assumes that an incoming visual image is compared with a library of prestored dimensionally isomorphic images, each of which has a name already associated with it. This theory is largely considered too simplistic, because the same stimulus can be viewed from multiple perspectives, thereby altering the input pattern, and. The hypothesis postulating that pattern recognition progresses by comparing an input sensory arousal pattern to cognitive pictures or symbolizations of patterns until a match is located. This mechanism plays a crucial role in how we identify objects, faces, and other stimuli, enabling quick recognition by matching incoming information to existing knowledge. Template matching involves comparing objects to stored templates, but it. Feature matching theory posits that objects are recognized by comparing their features to stored representations in memory, while template theory suggests that objects are recognized by matching incoming stimuli to specific templates or prototypes stored in memory. Template matching is the process by which the mind identifies objects by comparison to [a particular kind of] stored mental representation. Template matching, prototype matching, and feature analysis.Template Matching theory williamsonga.us
PPT Perception and Pattern Recognition PowerPoint Presentation, free
Template Matching theory williamsonga.us
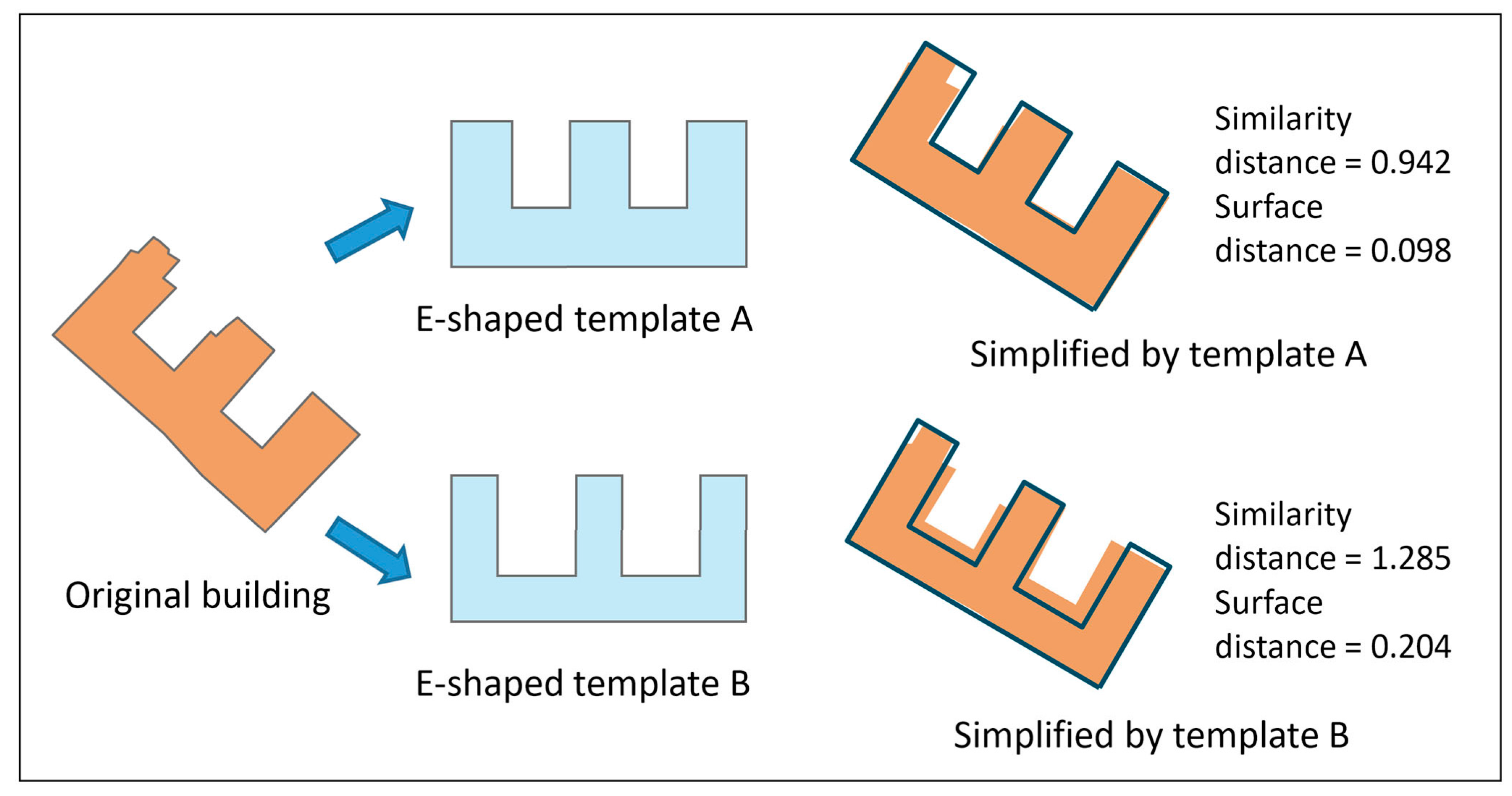
IJGI Free FullText Template Matching and Simplification Method for
PPT Chapter Four PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID613673
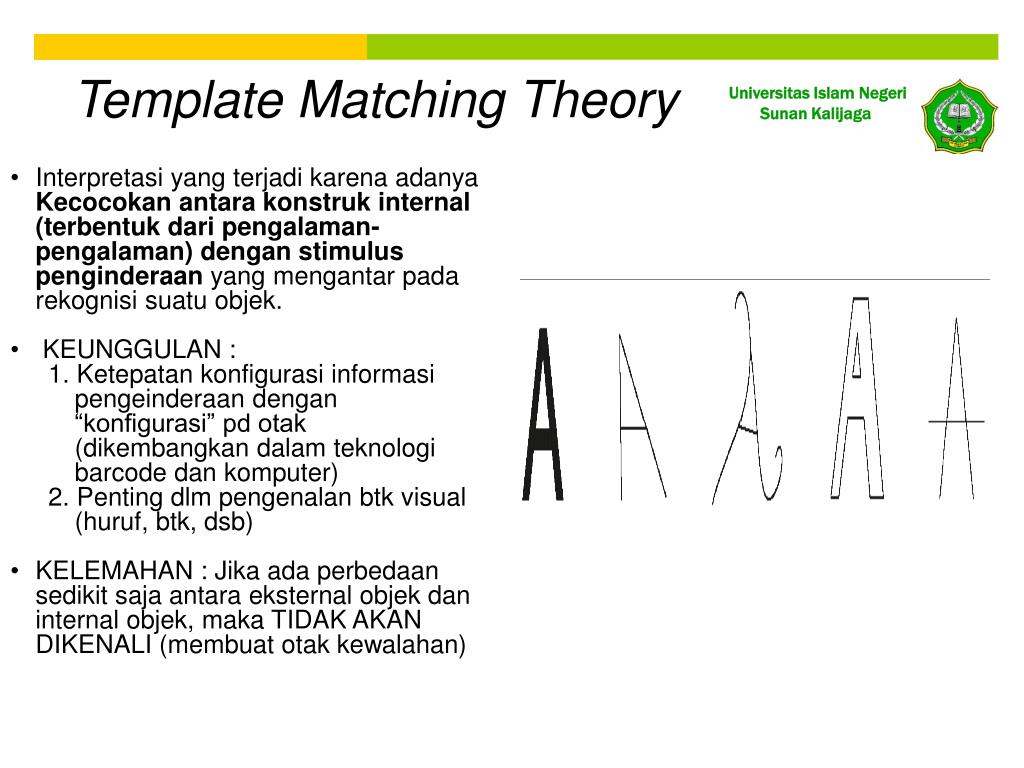
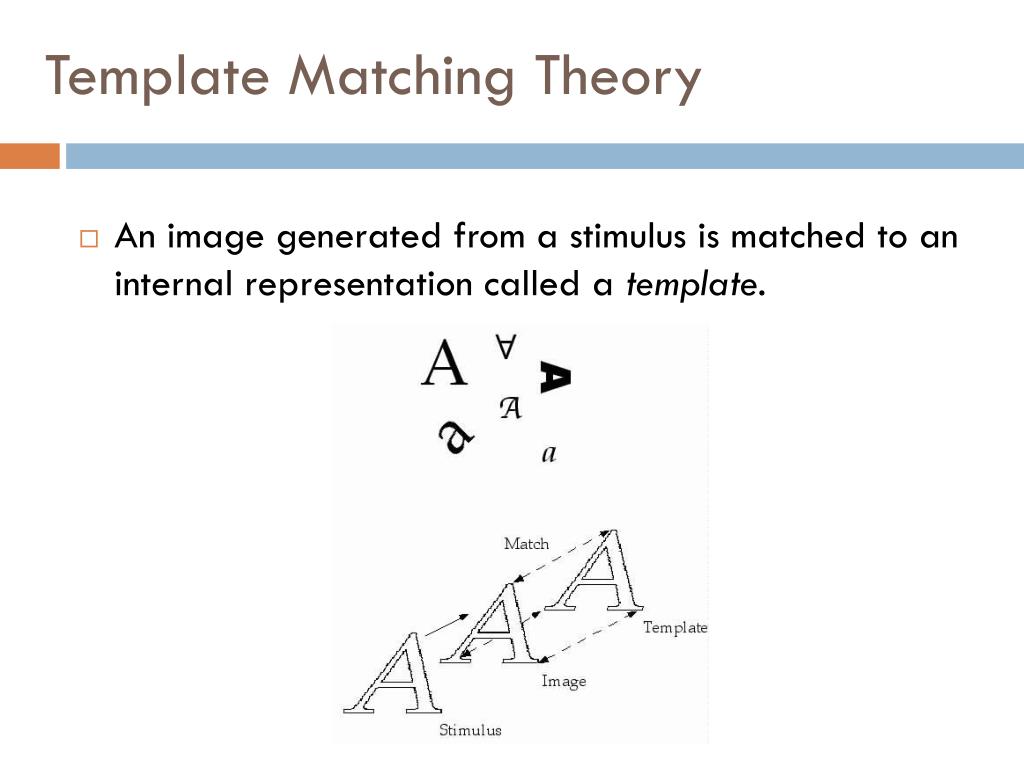
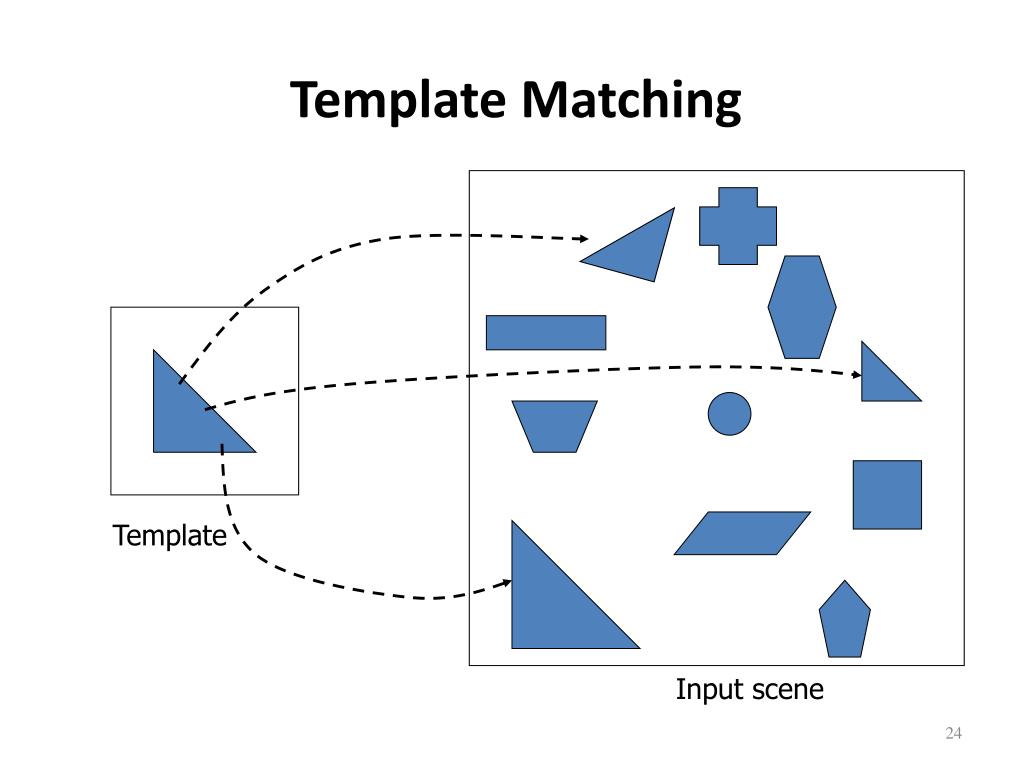
Template Matching Theory
PPT Chapter 3 Visual Perception PowerPoint Presentation, free
Template Matching Theory
Download Template Matching Theory Pattern Recognition free piratebayall
Template Matching Theory
The Application Of These Theories In Everyday Life Is Not Mutually Exclusive.
There Are Six Main Theories Of Pattern Recognition:
The Hypothesis That Pattern Recognition Proceeds By Comparing An Incoming Sensory Stimulation Pattern To Mental Images Or Representations Of Patterns (Templates) Until A Match Is Found.
Related Post: