Template Explicit Specialization In Cpp File
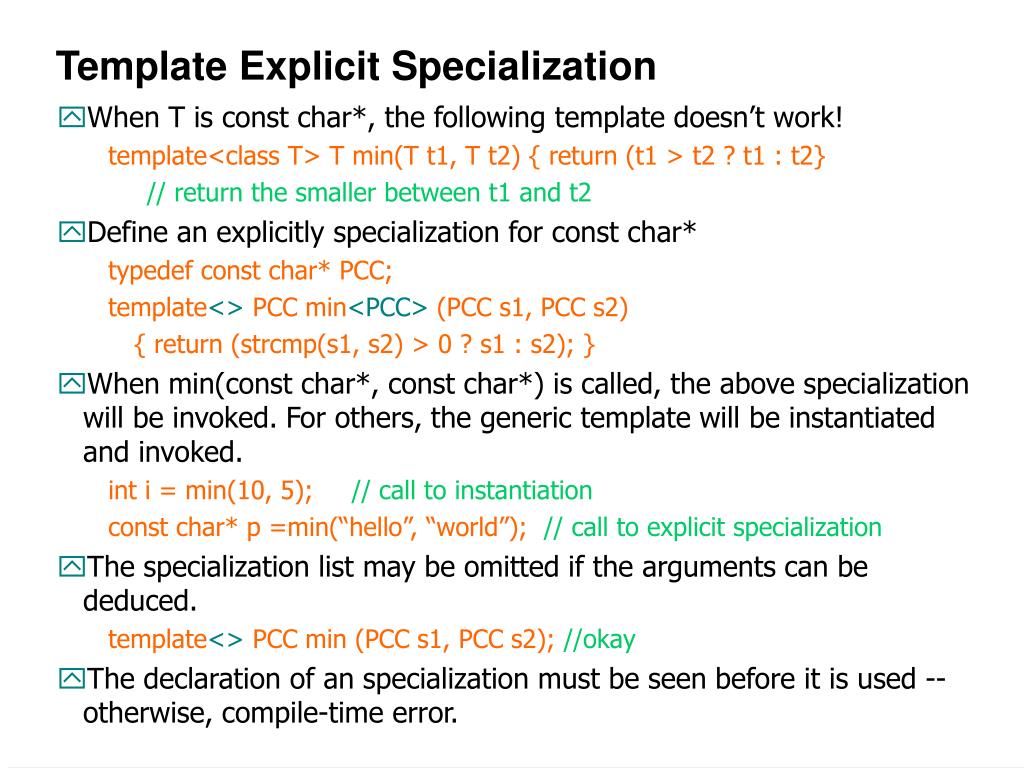
Template Explicit Specialization In Cpp File - When invoking the function in a hardened implementation, prior to any other. I'd recommend you to just put template definitions in your header file, or a.hpp file, but if you really want to there is a trick to get them in a seperate.cpp file. Template allows us to define generic classes and generic. This feature is particularly useful when. Explicit template specialization (often shortened to template specialization) is a feature that allows us to explicitly define different implementations of a template for specific. Template class foo { foo() = delete; You create an explicit instantiation by using the keyword template followed by the signature of the entity you want to instantiate. How do i explicitly select which version of a function template should get called? I have the following template class specializations in foo.h: With a function template, you can define special behavior for a specific type by providing an explicit specialization (override) of the function template for that type. When invoking the function in a hardened implementation, prior to any other. In an explicit specialization for such a member, there's a template <> for every enclosing class. The solution ends up being to move the explicit specialization from the header file to a code file. This is called template specialization. What is a “parameterized type”? However to make the other users of the header file not instance the default version, i needed. If a template, a member template or a member of a class template is explicitly specialized, a declaration of that specialization shall be reachable from every use of that. You create an explicit instantiation by using the keyword template followed by the signature of the entity you want to instantiate. // no definitions in the original template class typedef std::valarray.</p> This feature is particularly useful when. Member or a member template may be nested within many enclosing class templates. My template function does something special. With a function template, you can define special behavior for a specific type by providing an explicit specialization (override) of the function template for that type. // no definitions in the original template class typedef std::valarray.</p> Here i'm trying to create. This feature is particularly useful when. Conditions that the function assumes to hold whenever it is called. Here i'm trying to create a method template specialization for both c and d classes using the iscord concept. This entity can be a type or a member. Template specialization is the process of providing explicit implementations for templates to handle specific types. However to make the other users of the header file not instance the default version, i needed. Member or a member template may be nested within many enclosing class templates. The solution ends up being to move the explicit specialization from the header file to a code file. This entity can be a type or a member. Conditions that the. This is called template specialization. What is a “parameterized type”? Here i'm trying to create a method template specialization for both c and d classes using the iscord concept. This is definitely not a nasty hack, but be aware of the fact that you will have to do it (the explicit template specialization) for every class/type you want to use. The solution ends up being to move the explicit specialization from the header file to a code file. My template function does something special. When invoking the function in a hardened implementation, prior to any other. Using visionmethod = enum { templatematching,. It is possible in c++ to get a special behavior for a particular data type. This feature is particularly useful when. I have the following template class specializations in foo.h: With a function template, you can define special behavior for a specific type by providing an explicit specialization (override) of the function template for that type. Template allows us to define generic classes and generic. You create an explicit instantiation by using the keyword template. The solution ends up being to move the explicit specialization from the header file to a code file. This is called template specialization. Template class foo { foo() = delete; I'd recommend you to just put template definitions in your header file, or a.hpp file, but if you really want to there is a trick to get them in a. The solution ends up being to move the explicit specialization from the header file to a code file. Template specialization is the process of providing explicit implementations for templates to handle specific types differently. I have the following template class specializations in foo.h: I use the following command to compile it: // no definitions in the original template class typedef. This is called template specialization. This entity can be a type or a member. Member or a member template may be nested within many enclosing class templates. Template class foo { foo() = delete; It allows us to override the default behavior of a. If a template, a member template or a member of a class template is explicitly specialized, a declaration of that specialization shall be reachable from every use of that. Template specialization is the process of providing explicit implementations for templates to handle specific types differently. I'd recommend you to just put template definitions in your header file, or a.hpp file,. With a function template, you can define special behavior for a specific type by providing an explicit specialization (override) of the function template for that type. No, you don't need to put specializations in a separately compiled file, but, you need to beware that a specialized function template is just an ordinary function, because it's. This is definitely not a nasty hack, but be aware of the fact that you will have to do it (the explicit template specialization) for every class/type you want to use with the given template. In an explicit specialization for such a member, there's a template <> for every enclosing class. What is a “parameterized type”? If a template, a member template or a member of a class template is explicitly specialized, a declaration of that specialization shall be reachable from every use of that. Using visionmethod = enum { templatematching,. My template function does something special. // no definitions in the original template class typedef std::valarray.</p> When invoking the function in a hardened implementation, prior to any other. Template class foo { foo() = delete; It is possible in c++ to get a special behavior for a particular data type. Template specialization in c++ enables you to define a separate implementation for a template when it's instantiated with a specific type. Explicit template specialization (often shortened to template specialization) is a feature that allows us to explicitly define different implementations of a template for specific. Template allows us to define generic classes and generic. How do i explicitly select which version of a function template should get called?C++ Explicit specialization of a function template for a fully
C++ Explicit template specialization of member functions YouTube
C++ Template Specialization
Template specialization in C++ Coding Ninjas
Template specialization in C++ Coding Ninjas
PPT Introduction to C++ Programming Module 4 Function and Class
C++ Template Specialization
C++ Is it ok to write template specializations in a cpp file in this
Explicit Template Instantiation
Explicit Template Instantiation
I'd Recommend You To Just Put Template Definitions In Your Header File, Or A.hpp File, But If You Really Want To There Is A Trick To Get Them In A Seperate.cpp File.
It Allows Us To Override The Default Behavior Of A.
Here I'm Trying To Create A Method Template Specialization For Both C And D Classes Using The Iscord Concept.
This Feature Is Particularly Useful When.
Related Post: