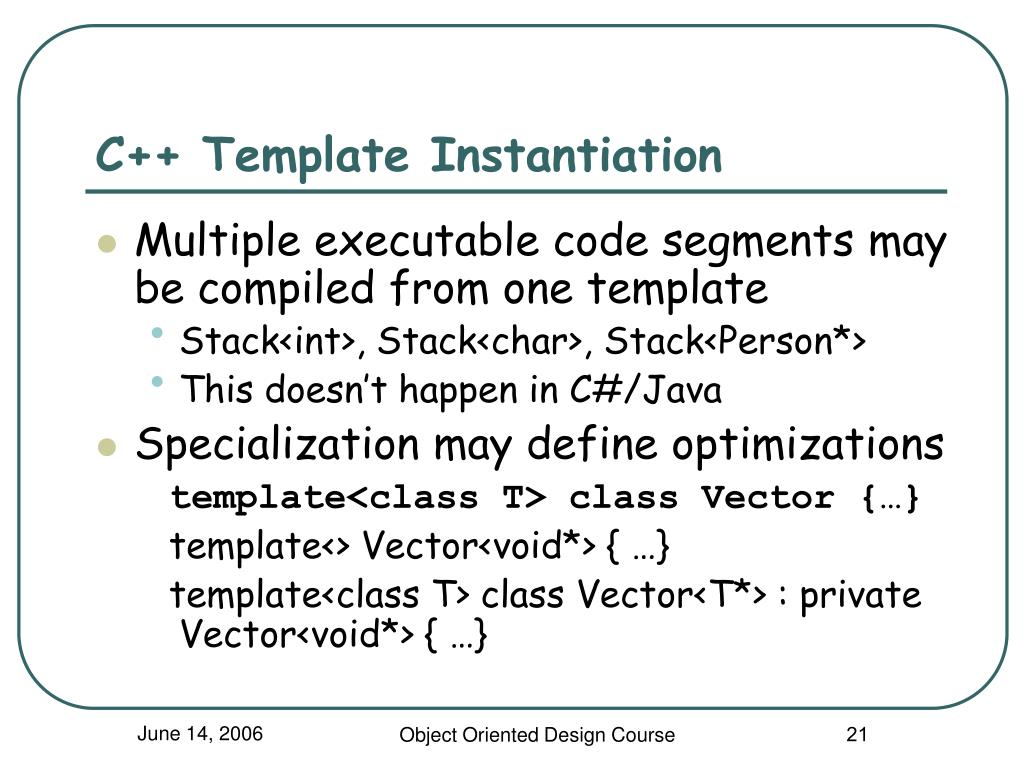
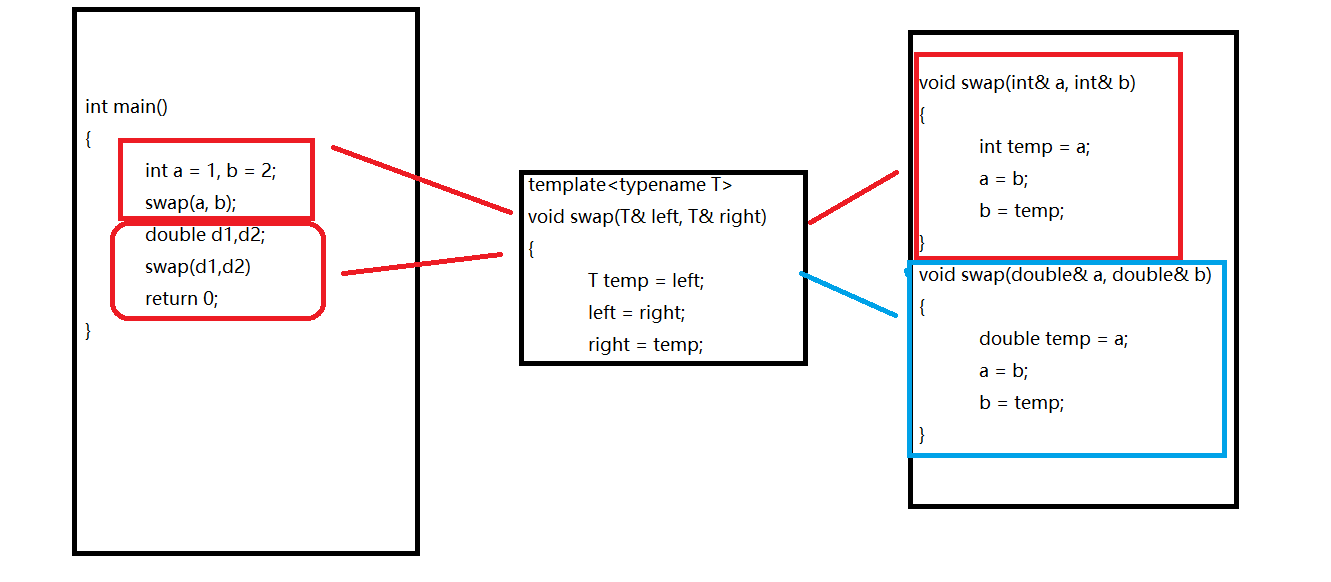
Explicit Template Instantiation
Explicit Template Instantiation - All you need is a. Template instantiation is creating a concrete function or a concrete class out of a function or class template. You create an explicit instantiation by using the keyword template followed by the signature of the entity you want to instantiate. In order for any code to appear, a template must be instantiated: You can explicitly tell the compiler when it should generate a definition from a template. Explicit instantiation is designed to optimize template libraries usage providing some of (mostly used) template instances in compiled binary form instead of source code. A member function, member class or static data member of a class template can be. Allows customizing the template code for a given set of template arguments. Explicit specialization may be declared in any scope where its primary template may be. This is called explicit instantiation. A member function, member class or static data member of a class template can be. However, we can add specialized template support through explicit template instantiation which will add the symbols needed to link (properly) against the library for use. This is called explicit instantiation. All you need is a. Explicit instantiation is designed to optimize template libraries usage providing some of (mostly used) template instances in compiled binary form instead of source code. Allows customizing the template code for a given set of template arguments. If a function template, variable template, member function template, or member function or static data member of a class template is explicitly instantiated with an explicit. In order for any code to appear, a template must be instantiated: In general you don't need to explicitly instantiate a template, but just define it in a header file and include that header file. You create an explicit instantiation by using the keyword template followed by the signature of the entity you want to instantiate. This entity can be a type or a member. This is called explicit instantiation. The template arguments must be provided so that the compiler can generate an actual class (or function,. Explicit instantiation of a function template or of a member function of a class template cannot use inline or constexpr. However, we can add specialized template support through explicit. The process of creating functions (with specific types) from function templates (with template types) is called function template instantiation (or instantiation for short). You can explicitly tell the compiler when it should generate a definition from a template. If the declaration of the explicit instantiation names an. This is called explicit instantiation. The template arguments must be provided so that. In order for any code to appear, a template must be instantiated: All you need is a. However, we can add specialized template support through explicit template instantiation which will add the symbols needed to link (properly) against the library for use. In general you don't need to explicitly instantiate a template, but just define it in a header file. A class, function, variable, or member template specialization can be explicitly instantiated from its template. In order for any code to appear, a template must be instantiated: This is called explicit instantiation. You can explicitly tell the compiler when it should generate a definition from a template. A member function, member class or static data member of a class template. You create an explicit instantiation by using the keyword template followed by the signature of the entity you want to instantiate. Explicit instantiation is designed to optimize template libraries usage providing some of (mostly used) template instances in compiled binary form instead of source code. The process of creating functions (with specific types) from function templates (with template types) is. A member function, member class or static data member of a class template can be. Allows customizing the template code for a given set of template arguments. Template instantiation is creating a concrete function or a concrete class out of a function or class template. You can explicitly tell the compiler when it should generate a definition from a template.. The template arguments must be provided so that the compiler can generate an actual class (or function,. This is called explicit instantiation. In general you don't need to explicitly instantiate a template, but just define it in a header file and include that header file. In order for any code to appear, a template must be instantiated: Explicit instantiation is. With explicit template instantiations, you can define a template and instantiate it in a dll, so clients don’t even have to see the implementation of the template. A member function, member class or static data member of a class template can be. All you need is a. This entity can be a type or a member. Template instantiation is creating. Allows customizing the template code for a given set of template arguments. In order for any code to appear, a template must be instantiated: The process of creating functions (with specific types) from function templates (with template types) is called function template instantiation (or instantiation for short). Explicit instantiation of a function template or of a member function of a. A class, function, variable, or member template specialization can be explicitly instantiated from its template. Explicit instantiation is designed to optimize template libraries usage providing some of (mostly used) template instances in compiled binary form instead of source code. Explicit specialization may be declared in any scope where its primary template may be. The following are examples of explicit instantiations:. All you need is a. You can explicitly tell the compiler when it should generate a definition from a template. Explicit specialization may be declared in any scope where its primary template may be. The process of creating functions (with specific types) from function templates (with template types) is called function template instantiation (or instantiation for short). Explicit instantiation of a function template or of a member function of a class template cannot use inline or constexpr. A member function, member class or static data member of a class template can be. However, a common application of explicit template. Explicit instantiation is designed to optimize template libraries usage providing some of (mostly used) template instances in compiled binary form instead of source code. If a function template, variable template, member function template, or member function or static data member of a class template is explicitly instantiated with an explicit. The template arguments must be provided so that the compiler can generate an actual class (or function,. With explicit template instantiations, you can define a template and instantiate it in a dll, so clients don’t even have to see the implementation of the template. Allows customizing the template code for a given set of template arguments. In order for any code to appear, a template must be instantiated: The following are examples of explicit instantiations: However, we can add specialized template support through explicit template instantiation which will add the symbols needed to link (properly) against the library for use. In general you don't need to explicitly instantiate a template, but just define it in a header file and include that header file.Learn What Is Explicit Instantiation of a Template in C++
C++ Force explicit template instantiation with CRTP YouTube
Explicit Template Instantiation
Explicit Template Instantiation
Explicit Template Instantiation
Explicit Template Instantiation
Explicit Template Instantiation
Explicit Template Instantiation
Explicit Template Instantiation
Explicit Template Instantiation
Template Instantiation Is Creating A Concrete Function Or A Concrete Class Out Of A Function Or Class Template.
A Class, Function, Variable, Or Member Template Specialization Can Be Explicitly Instantiated From Its Template.
You Create An Explicit Instantiation By Using The Keyword Template Followed By The Signature Of The Entity You Want To Instantiate.
This Entity Can Be A Type Or A Member.
Related Post: